Gambling Winnings Subject To Self Employment Tax
- Are Lottery Winnings Subject To Self Employment Tax
- Gambling Winnings Subject To Self Employment Taxes
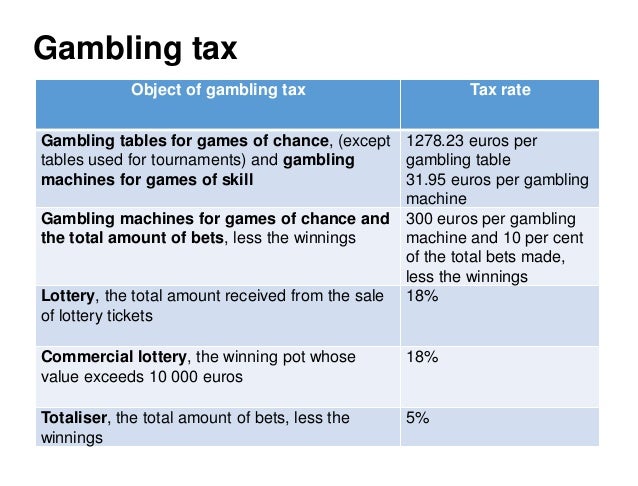
First let's look at self-employment taxes: As a casual gambler there's no self-employment tax. As a professional gambler your net winnings are subject to self-employment tax. Net winnings are the amount remaining after all offsetting gambling wagers (losses) and after other allowable expenses such as travel, meals, and so on. Additionally, you will have to pay self-employment tax on your winnings that casual gamblers are not subject to. What Gambling Winnings Are Classified as Income? You are required to report any winnings from lotteries, raffles, horse races, or casino gambling as income. It doesn't matter whether your winnings are in the form of cash or prizes.
Taxes are probably the last thing on your mind during an exciting gambling session. However, they inevitably come up following a big win or profitable year.
You may have two main questions at this point:
- Do I need to pay taxes on my wins?
- If so, how much do I have to pay?
The following guide discusses whether your gambling wins are taxable and other important topics regarding this subject.
The Short Answer Is Yes
I’ll cut right to the chase: yes, you do need to pay federal taxes on gambling winnings in the United States. This is especially true when you net a big win and receive a W-2G form.
According to the IRS, a gambling establishment should issue a W-2G when you win an amount that’s subject to federal income tax withholding (24% of win).
Slot machines present a famous example of when you’ll receive a W-2G form after winning so much. Casinos must issue a form when you win a prize worth $1,200 or more through slots or video poker.
As for the second point, a sportsbook or racetrack must withhold federal taxes when you win a bet worth 300x your initial stake. If you wager $5 and win $3,000, for example, then the bookmaker will issue a W-2G form and withhold $720 (24%).
Here’s a broader look at the W-2G and tax withholding threshold for different types of gambling:
- $600+ through sportsbooks and racetracks (provided it’s 300x your stake).
- $1,200+ through a slot machine, video poker machine, or bingo game.
- $1,500+ through keno.
- $5,000+ through a poker tournament.
All Winnings Are Subject to Taxation
Technically, you’re supposed to report any gambling winnings—big or small. Even if you win $20 in an office betting pool, the IRS wants to know about it.
If you want to stay above board, then you should report all wins on Form 1040 (under “other income”). As I’ll cover later, you can deduct losses from winnings as well.
Furthermore, any amount that’s withheld by a casino, poker room, sportsbook, or racetrack is deducted from what you owe. Gambling establishments keep 24% of a win when they do withhold money.
W-2G Forms Don’t Apply to Table Games
You’ll receive a W-2G when earning big wins through most types of gambling. However, casino table games are an exception to the norm.
Unlike a jackpot game (e.g. video poker) or a poker tournament, casinos have no idea how much money you start with in a table game. Therefore, they can’t really determine when you do and don’t experience big wins.
Examples of table games that are exempt from W-2G forms include:
- Baccarat
- Blackjack
- Caribbean stud
- Craps
- Roulette
- Three-card poker
The IRS still expects you to pay taxes on profits earned through table games. Again, though, the casino can’t issue a W-2G because they can’t tell how much money you’ve actually won.
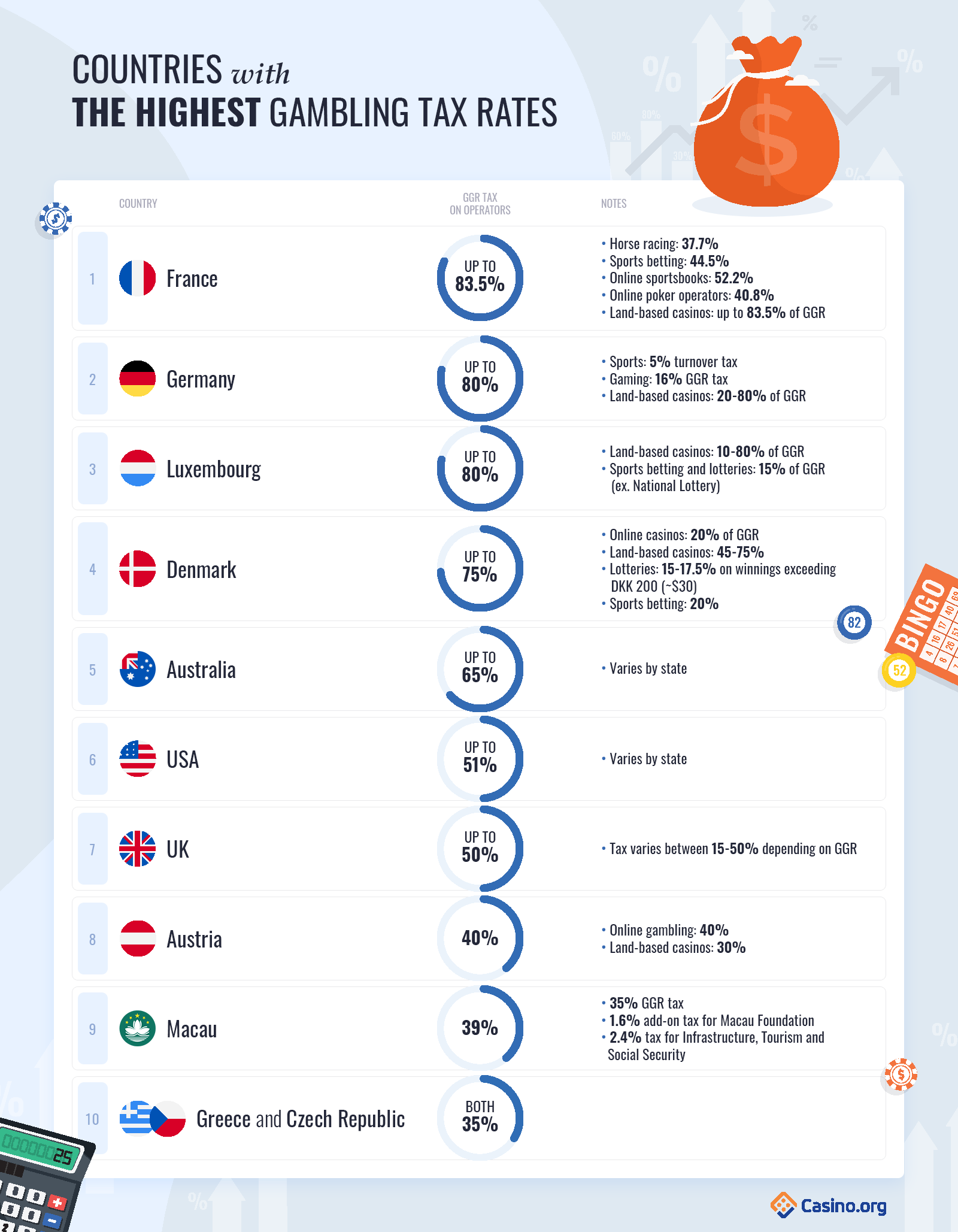
Some States Tax Gambling Winnings
Most states tax your income, including gambling winnings. Depending upon where you live, you’ll probably need to pay taxes to both the IRS and your state.
For Example:Michigan features a 4.25% flat income tax. The Wolverine State expects you to pay this same 4.25% rate on gambling wins.
West Virginia, on the other hand, doesn’t tax your winnings. Casinos/sportsbooks in the Mountaineer State only withhold federal taxes (when necessary).
Assuming you travel to another state to gamble, you may have two states wanting taxes. Luckily, though, you won’t be subject to double taxation.


Instead, your home state will give you credit for whatever taxes are paid to the state where the winnings occurred.
Can You Deduct Losses?

You can deduct gambling losses from winnings. However, these deductions are itemized rather than standard deductions.
Here’s an example to explain:
- You win $5,000 through sports betting.
- You lose $4,500.
- You must report the full $5,000—not $500 (5,000 – 4,500)—under other income.
- Meanwhile, the $4,500 is reported through various itemized deductions.
In short, itemized deductions are expenses that reduce your taxable income. The standardized variety includes flat-dollar, common deductions.
You may be able to save more money through itemized deductions. However, standard deductions are easier to deal with and also have the potential to save you more money.
Regardless, you must use itemized deductions when dealing with losses. This means spending more time on your tax returns or working with an accountant.
Keep in mind that you won’t receive a tax refund for gambling losses. Instead, you can only deduct an amount equal to your winnings each year. If you win $3,500, for example, then you can’t deduct more than $3.5k and expect a return.
Keep Records on Wins & Losses
The IRS may take your word at face value when it comes to gambling. Of course, they also have the ability to audit you when they deem it necessary.
That said, you don’t want to guestimate on your wins and losses. Instead, you want proof through the form of records.
Journals offer a great way to record your gambling activities. You can log the following for each entry:
- Date of gambling session
- Location of the establishment
- Game played
- Starting bankroll
- Ending bankroll
Such entries don’t guarantee you’re being honest. However, they at least show the IRS that you’re making a legitimate attempt at recordkeeping.
You can take your recordkeeping efforts even further by holding onto any other relevant documents. Betting slips, winning tickets, canceled checks, bank statements, W-2G forms, and anything else of relevance are all worth saving.
Are Lottery Winnings Subject To Self Employment Tax
What Happens If You Don’t Report Gambling Winnings?
The IRS fully expects you to report gambling winnings and especially annual profits. They don’t take kindly to you failing to report these wins.
Of course, you’re unlikely to draw an audit for winning a $25 sports bet. You stand a higher chance of being audited, though, if you win enough for a W-2G form.
In this case, the casino/sportsbook/racetrack also sends a copy of the from to the IRS. The latter features reliable software that can match up your reported income with documentation of nonreported income.
Assuming you fail to report gambling winnings, then the IRS may do little more than send a letter and issue a small fine. You should definitely pay up, or at least work out a payment plan, in this case.
You’ll face more serious consequences, though, if you fail to report a huge win and lie about the matter when/if caught. Refusal to pay and/or heavy efforts to cover up the deceit will lead to bigger fines and possibly jail time.
Gamblers Stand Increased Chances of an Audit
Nobody likes attracting an audit from the IRS. Unfortunately, the chances of being audited increase for gamblers.
This is especially true when you net a big win and receive a W-2G. Of course, you can reduce the odds of being audited by claiming anything on the form.
The IRS may also become suspicious if you claim big losses on your tax return. You’ll put the taxman on increased alert when winning a huge prize (e.g. $50,000) and claiming a matching amount of losses.
Also, you can’t write off hotel stays, meals, and entertainment as a casual gambler. You must be a professional to claim such itemized deductions.
How Do Professional Gamblers Report Winnings?
Pro gamblers claim winnings on Schedule C as a self-employed person rather than as other income on Form 1040.
Even as a professional, you can’t deduct more losses than winnings in a year. You’re stuck in a tough situation with treating gambling as a day job, yet not being able to file losses that exceed winnings.
As mentioned before, though, you’re able to deduct business expenses like hotel stays and meals. These expenses just need to be a legitimate part of your business.
Conclusion
In answer to the original question, yes, you’re supposed to claim real money gambling winnings on federal tax forms. Even if you end up losing money on the year, the IRS wants to see your wins and losses.
Of course, tax collectors don’t care a great deal when you win $200 on the year. They spend most of their time looking for bigger winners.
The times when you want to be especially diligent in this matter include:
- When you book a large win and receive a W-2G form.
- If you win a significant amount of profits throughout the year.
- When you win 600x your bet with a sports or horse wager.
Again, the IRS and your state (if applicable) expect all gambling winnings to be reported. But you can use some commonsense in deciding when reporting wins are truly necessary.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.To this point, this blog has focused on how the taxpayer determines his/her taxable gambling winnings. This week’s post about the self-employment tax begins the discussion regarding how the IRS gets its bite on those winnings. To professional gamblers and poker coaches, the self-employment tax is a big player.
Self-employment tax is a social security and Medicare tax. Self-employment tax is imposed on self-employment income, which equals the net earnings from self-employment derived by an individual, other than nonresident aliens, during the tax year. Net earnings from self-employment derived by an individual is the gross income derived by an individual from any trade or business carried on by the individual, reduced by income tax deductions attributable to the trade or business. Next week’s post will be dedicated to tax deductions attributable to the trade or business of gambling.
Today’s first takeaway: Because professional gamblers, but not recreational gamblers, are engaged in the trade or business of gambling, professional gamblers must report and pay self-employment tax on gambling winnings, but recreational gamblers do not. Also, generally speaking, income earned from poker coaching is subject to the self-employment tax.
Imposing the self-employment tax makes sense: If you earn wages from an employer, that employer is required to withhold a portion of your income for social security and Medicare and pay it to Uncle Sam. These withheld amounts are called withholding taxes. If you earn income for yourself, there is no employer withholding the tax. The rough equivalent to withholding tax is the self-employment tax.
There are two elements to self-employment tax: (1) social security (old-age, survivors, and disability insurance); and (2) Medicare (hospital insurance). Generally, self-employment income is taxed at a rate of 12.4% for the first element, and at a rate of 2.9% for the second element, totaling a rate of 15.3%. Note that one-half of the self-employment tax is allowable as a deduction in computing adjusted gross income. Also note that if total net earnings from self-employment for the tax year are less than $400, there is no self-employment tax.
Those are the general rules regarding how to figure out the self-employment tax amount. The next point to discuss is how to report self-employment income and pay the tax thereon.
Today’s second takeaway:A taxpayer expecting to owe self-employment tax of $1,000 or more for the tax year generally has to make estimated tax payments during the tax year. A taxpayer must also attach a Schedule SE to his/her Form 1040 when filing for the year.
Federal income tax is a pay-as-you-go tax. Taxpayers must pay tax as income is earned or received during the year. Tax is paid either by withholding or estimated taxes. As discussed, professional gamblers do not have their winnings withheld, so they must make estimated tax payments if they expect to owe tax of $1,000 or more when filing.
Gambling Winnings Subject To Self Employment Taxes
To ascertain estimated tax, the taxpayer must figure out expected adjusted gross income taxable income, taxable income, taxes, deductions, and credits for the year. Typically, using the prior year’s income, deductions, and credits is a good starting point. Of course, if you plan to double or triple the amount of time spent playing online poker from the previous year, you should take that into consideration. Form 1040-ES has a worksheet to figure out estimated tax.
There are four payment periods for estimated tax payments during each tax year. Yes, that means taxpayers with self-employment income must make estimated tax payments to the IRS four times a year. If the taxpayer does not pay enough tax by each of the due dates, penalties may be imposed.
Ultimately, don’t treat the self-employment tax lightly. If you are a professional gambler or a poker coach and haven’t been keeping up with estimated tax payments, you should start doing so.